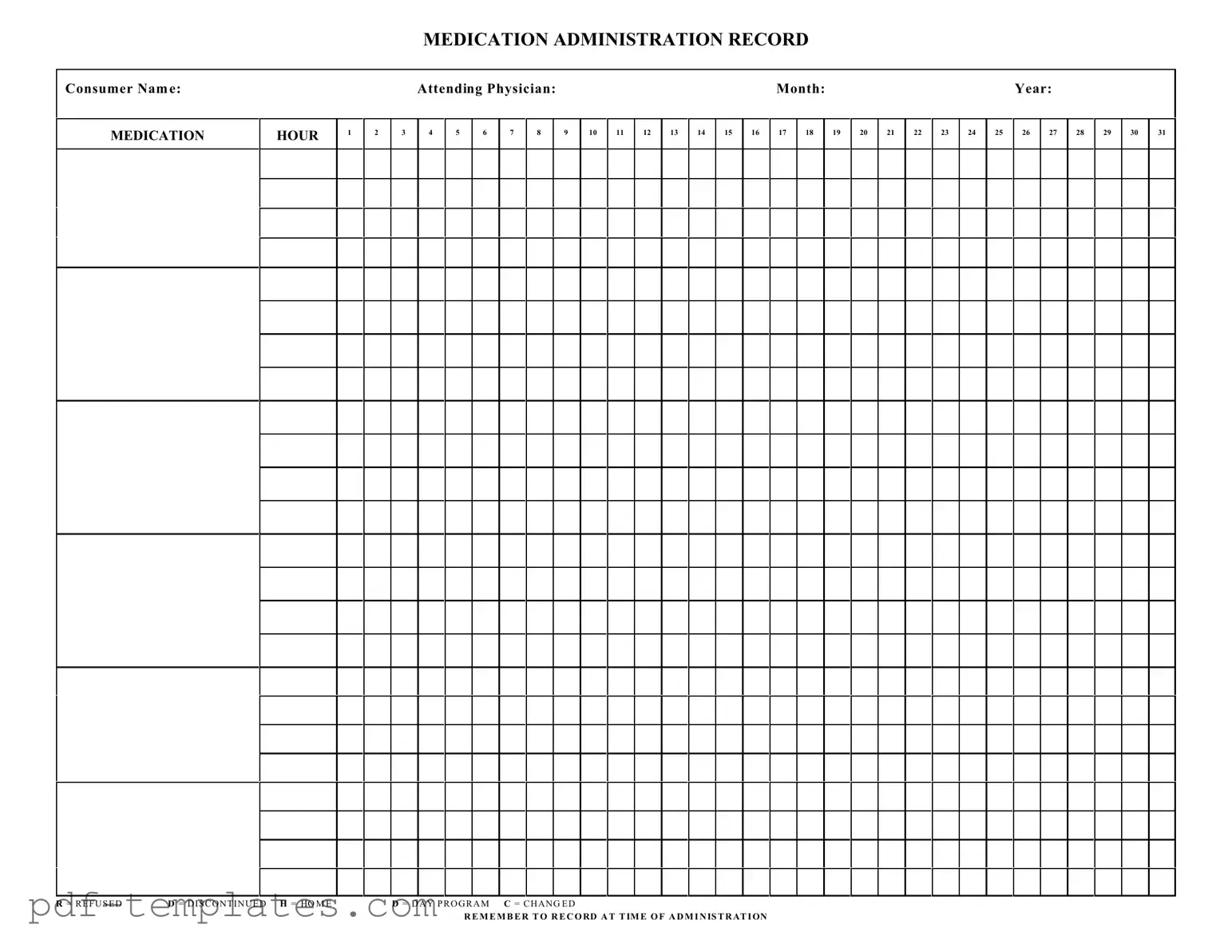
Get Medication Administration Record Sheet Form in PDF
The Medication Administration Record Sheet is a crucial tool in healthcare settings, ensuring that patients receive their medications safely and effectively. This form captures essential information, including the consumer's name, the attending physician, and the specific month and year of administration. It is designed to track medication doses given at various hours throughout the day, providing a clear timeline for healthcare providers. Each hour of the day is marked, allowing for easy recording of whether a medication was administered, refused, or discontinued. Symbols such as "R" for refused, "D" for discontinued, and "H" for home help staff quickly identify the status of each medication. Additionally, the form emphasizes the importance of recording the time of administration, which is vital for maintaining accurate medical records and ensuring patient safety. By using this structured approach, healthcare providers can enhance communication, reduce errors, and improve overall patient care.
Misconceptions
Several misconceptions exist regarding the Medication Administration Record (MAR) Sheet form. Understanding these can help ensure proper usage and compliance.
- Misconception 1: The MAR Sheet is only for nurses.
- Misconception 2: The MAR Sheet does not require updates once filled out.
- Misconception 3: All medications must be administered at the same time each day.
- Misconception 4: Refused medications do not need to be recorded.
This is incorrect. While nurses often complete the MAR Sheet, other healthcare professionals involved in medication administration can also use it. This includes pharmacists and attending physicians.
This is false. The MAR Sheet must be updated regularly to reflect any changes in medication orders, dosages, or administration times. Accurate record-keeping is essential for patient safety.
This is not necessarily true. While some medications do require strict adherence to timing, others may have more flexible schedules. The MAR Sheet should reflect the specific instructions provided by the physician.
This is incorrect. Any refusal of medication must be documented on the MAR Sheet. This ensures that all healthcare providers are aware of the patient's compliance and can address any issues that arise.
Medication Administration Record Sheet: Usage Instruction
Completing the Medication Administration Record Sheet is essential for tracking medication administration accurately. Follow these steps to ensure all necessary information is recorded correctly.
- Begin by writing the Consumer Name at the top of the form.
- Next, fill in the Attending Physician name in the designated space.
- Record the Month and Year for which the medication is being administered.
- Identify the HOUR columns. Mark the appropriate hour for each medication administration.
- In the daily sections (1-31), enter the medications administered for each day of the month.
- If a medication was refused, write R in the corresponding box. For discontinued medications, use D. If the medication was changed, enter C.
- Make sure to record at the time of administration for accuracy.
After completing the form, it is crucial to review the entries for any errors or omissions. This ensures that the medication administration process remains safe and effective.
Common mistakes
-
Not including the consumer name at the top of the form. This is essential for identifying the individual receiving medication.
-
Failing to fill out the attending physician's name. This information is crucial for tracking who prescribed the medication.
-
Overlooking the month and year fields. These dates help in maintaining accurate records and ensuring proper medication management.
-
Incorrectly marking the medication hour. Accurate timing is vital for effective medication administration.
-
Using abbreviations or symbols that are not standard. Clarity is key, and it is important to ensure that all staff can understand the entries.
-
Neglecting to record the time of administration. This step is critical for monitoring medication effectiveness and compliance.
-
Failing to indicate if a dose was refused or discontinued. These notations are important for tracking patient adherence and medication history.
-
Not documenting changes in medication. If a medication is changed, it should be clearly noted to avoid confusion.
-
Forgetting to sign or initial the form after administration. This serves as verification that the medication was given as prescribed.
-
Leaving blank spaces where information should be recorded. Each section should be completed to ensure comprehensive documentation.
File Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Medication Administration Record Sheet is designed to document the administration of medications to consumers, ensuring accurate tracking and accountability. |
| Consumer Identification | Each record includes fields for the consumer's name, allowing for clear identification and reducing the risk of medication errors. |
| Monthly Tracking | The form is structured to cover an entire month, with designated spaces for each day, facilitating comprehensive medication management. |
| Administration Time | Providers are reminded to record the time of administration, which is critical for monitoring medication effectiveness and adherence. |
| State Regulations | In many states, such as California, the use of a Medication Administration Record is governed by the California Code of Regulations, Title 22, Section 87465. |
| Abbreviations | The form includes standard abbreviations (e.g., R for Refused, D for Discontinued) to streamline documentation and enhance clarity. |
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Medication Administration Record Sheet form, it is important to follow certain guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Below are six recommendations.
- Do write the consumer's name clearly at the top of the form.
- Do record the date accurately, including the month and year.
- Do indicate the attending physician's name to ensure proper oversight.
- Do document each medication administration at the time it occurs.
- Don't leave any sections of the form blank; complete all required fields.
- Don't use abbreviations that may lead to confusion; write out terms fully.
Similar forms
The Medication Administration Record (MAR) is similar to the Patient Medication List, which serves as a comprehensive inventory of all medications a patient is currently taking. This document is essential for healthcare providers to ensure that they are aware of any potential drug interactions and to maintain an accurate medication history. Just like the MAR, the Patient Medication List requires updates whenever there are changes in the patient's medication regimen, thereby supporting safe and effective medication management.
Understanding the importance of accurate documentation in healthcare is crucial, as it not only ensures the proper administration of treatments but also reinforces the accountability of care providers. One essential form in this regard is the USCIS I-864 form, which can be explored further at documentonline.org/blank-uscis-i-864, highlighting the importance of financial support in the immigration process, echoing the structured approach required in patient care documentation.
Another document akin to the MAR is the Medication Reconciliation Form. This form is utilized during transitions of care, such as hospital admissions or discharges, to ensure that a patient’s medication orders are accurate and complete. Similar to the MAR, the Medication Reconciliation Form helps prevent medication errors by comparing the medications a patient is currently taking with those prescribed by their healthcare provider. Both documents emphasize the importance of clear communication and meticulous record-keeping in promoting patient safety.
The Treatment Administration Record (TAR) also shares similarities with the MAR. The TAR is used primarily in settings like long-term care facilities to document the administration of various treatments, including medications, therapies, and procedures. Both the TAR and MAR require diligent record-keeping to track what has been administered, when, and by whom. This ensures that all healthcare providers involved in a patient's care have access to accurate and up-to-date information, thereby enhancing the quality of care provided.
Lastly, the Nursing Care Plan can be compared to the MAR in that both documents play crucial roles in patient care management. The Nursing Care Plan outlines the specific interventions and goals for a patient’s care, including medication administration. While the MAR focuses on documenting the actual administration of medications, the Nursing Care Plan provides a broader context, detailing how those medications fit into the overall treatment strategy. Both documents are essential for ensuring that patient care is coordinated, comprehensive, and effective.
Other PDF Forms
How to Check How Many College Credits You Have - Class attendance and grades are typically included in the transcript details.
In addition to the requirements for filing the CA DMV SR1 form, it's advisable for residents to familiarize themselves with other necessary documentation, which can be found under All California Forms, ensuring compliance with state regulations and avoiding any lapses in legal driving status.
Texas Temporary Tag - Use this form as an interim solution for vehicle registration.