Get Hazard Bill Of Ladden Form in PDF
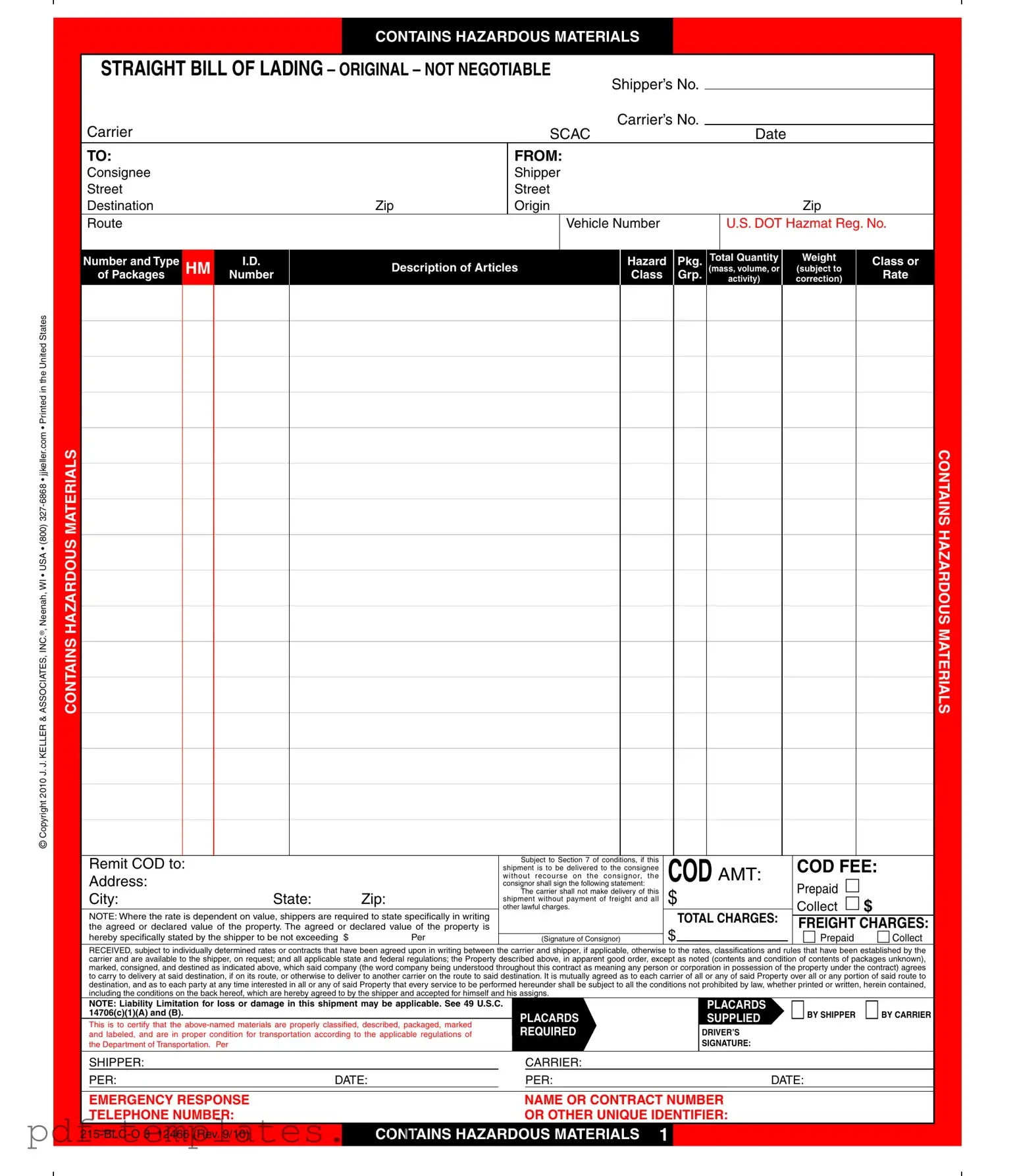
The Hazard Bill of Lading form serves as a critical document in the transportation of hazardous materials, ensuring compliance with federal regulations while facilitating safe and efficient shipping practices. This form captures essential details, including the shipper's and consignee's information, the description of the hazardous materials being transported, and the associated weight and quantity. The document also specifies the transportation route and vehicle number, along with the U.S. DOT Hazmat registration number, which is vital for regulatory compliance. Notably, the form outlines payment terms, including options for prepaid or collect charges, and includes a section for the consignor's declaration of the property's value. Additionally, it emphasizes the carrier's liability limitations and the responsibilities of both the shipper and carrier in the event of loss or damage during transit. The Hazard Bill of Lading not only aids in the documentation of hazardous shipments but also ensures that all parties involved are aware of their obligations and rights under the law, thus promoting a safer transportation environment.
Misconceptions
- Misconception 1: The Hazard Bill of Lading is only necessary for hazardous materials.
- Misconception 2: Signing the bill of lading means the shipper has no liability.
- Misconception 3: Once the bill of lading is signed, it cannot be changed.
- Misconception 4: The carrier is always liable for loss or damage during transport.
- Misconception 5: The bill of lading guarantees delivery on time.
- Misconception 6: The shipper does not need to declare the value of the property.
- Misconception 7: The bill of lading is not important for hazardous materials.
- Misconception 8: The shipper can ignore the terms and conditions once the shipment is in transit.
This form is essential for all types of shipments, not just those containing hazardous materials. It serves as a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions of the transport, regardless of the cargo type.
In reality, the shipper retains certain responsibilities, including ensuring that the information provided is accurate. Liability can still apply, especially if incorrect information leads to issues during transport.
While changes can be challenging, it is possible to amend the bill of lading. However, both parties must agree to any modifications, and these should be documented properly.
The carrier's liability is limited under certain conditions. Factors such as acts of God, public enemy actions, or defects in the property itself can exempt the carrier from liability.
Delivery times are not guaranteed. The carrier is only required to deliver the property with reasonable dispatch, which may vary based on circumstances beyond their control.
Shippers must declare the value of the property being transported, especially if the rate is dependent on that value. Failing to do so can limit recovery in the event of loss or damage.
This document is crucial for hazardous materials. It ensures compliance with regulations and protects all parties involved by clearly outlining the responsibilities and liabilities associated with the shipment.
All parties must adhere to the terms and conditions specified in the bill of lading throughout the transport process. Ignoring these can lead to legal complications and financial repercussions.
Hazard Bill Of Ladden: Usage Instruction
Filling out the Hazard Bill of Lading form is essential for ensuring that hazardous materials are transported safely and in compliance with regulations. This step-by-step guide will help you complete the form accurately.
- Shipper Information: Fill in the shipper's name and address in the designated fields. Include the shipper's number if applicable.
- Carrier Information: Enter the carrier's name and the carrier's number. The SCAC (Standard Carrier Alpha Code) should also be included.
- Date: Write the date when the form is completed.
- Consignee Information: Provide the consignee's name and address, including street, city, state, and zip code.
- Origin Information: Fill in the origin address, including street, city, state, and zip code.
- Vehicle Number: Enter the vehicle number that will transport the shipment.
- U.S. DOT Hazmat Registration Number: Include the registration number for hazardous materials.
- HM ID: Specify the hazardous materials identification number.
- Description of Articles: Clearly describe the hazardous materials being shipped.
- Hazard Class: Indicate the hazard class of the materials, using the appropriate codes.
- Total Quantity: State the total quantity of packages being shipped.
- Weight: Provide the total weight of the shipment, specifying the unit of measure (mass or volume).
- Charges: Fill in the prepaid or collect charges, including COD amounts and fees if applicable.
- Signature of Consignor: The consignor must sign the form to acknowledge the terms and conditions.
- Emergency Response Information: Include the name, contract number, and telephone number for emergency response.
Once the form is filled out, ensure that all information is accurate. This will help prevent delays or issues during transportation. After verification, the form should be submitted to the carrier along with the hazardous materials for shipping.
Common mistakes
-
Failing to accurately identify the consignee and shipper information. This can lead to significant delays in delivery.
-
Not providing a complete description of the hazardous materials. Each item must be clearly identified to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
-
Omitting the U.S. DOT Hazmat Reg. No.. This number is crucial for proper handling and transportation of hazardous materials.
-
Incorrectly stating the total quantity and weight of the packages. Discrepancies can result in additional fees or complications during transit.
-
Neglecting to check the appropriate hazard class for the materials being shipped. Each class has specific regulations that must be followed.
-
Forgetting to indicate whether the shipment is prepaid or collect. This detail affects payment responsibilities and can lead to misunderstandings.
-
Not signing the required statement regarding payment of freight and charges. This signature is essential for the carrier to proceed with delivery.
-
Leaving out the emergency response contact information. This information is vital in case of an incident during transportation.
-
Failing to provide a declared value for the shipment. This value impacts liability and compensation in the event of loss or damage.
-
Not reviewing the form for accuracy before submission. Simple errors can lead to significant issues down the line.
File Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Origin | This form is produced by J. J. Keller & Associates, Inc., located in Neenah, Wisconsin, USA. |
| Form Type | It is a Hazardous Materials Straight Bill of Lading, which is not negotiable. |
| Contact Information | For inquiries, you can reach J. J. Keller at (800) 327-6868. |
| Hazardous Materials | The form is specifically designed for shipments that contain hazardous materials. |
| Liability Limitations | The carrier may limit liability for loss or damage, as outlined in the terms and conditions. |
| Claim Filing | Claims for loss or damage must be filed within nine months of delivery. |
| Freight Charges | The shipper is primarily responsible for all freight and lawful charges unless otherwise specified. |
| Emergency Response | Emergency response information must be provided, including a contact number. |
| Governing Law | Applicable federal regulations, including 49 U.S.C. § 13706, govern this bill of lading. |
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Hazard Bill of Lading form, it's essential to be thorough and accurate. Here’s a guide on what to do and what to avoid:
- Do double-check all information before submission to ensure accuracy.
- Do clearly indicate the nature of the hazardous materials being shipped.
- Do sign the form to acknowledge your understanding of the terms and conditions.
- Do keep a copy of the completed form for your records.
- Do provide emergency contact information for any potential incidents.
- Don't leave any sections blank; incomplete forms can lead to delays.
- Don't misrepresent the contents of the shipment; this can have serious legal implications.
- Don't forget to include the proper packaging details for hazardous materials.
- Don't submit the form without verifying that all required signatures are present.
- Don't ignore the specific regulations related to hazardous materials transportation.
Similar forms
The Hazard Bill of Lading form shares similarities with the standard Bill of Lading, which serves as a receipt for goods and a contract between the shipper and carrier. Both documents detail the terms of transportation, including the description of goods, shipping instructions, and liability clauses. However, the Hazard Bill of Lading specifically addresses hazardous materials, requiring additional information about safety and compliance with regulations. This added layer of detail is crucial for ensuring the safe handling and transport of dangerous goods.
Another document similar to the Hazard Bill of Lading is the Freight Bill. While the Freight Bill primarily outlines the charges associated with the shipment, it also serves as proof of the transaction between the shipper and the carrier. Like the Hazard Bill, it requires accurate information about the shipment, including weight and destination. However, it lacks the specific regulations and safety requirements that apply to hazardous materials, making the Hazard Bill more complex in nature.
To facilitate the sale of firearms in Texas, you can find valuable insight in our guide on the essential aspects of the Firearm Bill of Sale. For more details, visit our comprehensive guide on the Firearm Bill of Sale.
The Shipping Manifest is another related document that lists all the items being shipped. It serves as a comprehensive inventory, detailing each item’s description, quantity, and destination. Similar to the Hazard Bill of Lading, the Shipping Manifest is essential for tracking shipments. However, it does not specifically address the handling of hazardous materials, which the Hazard Bill explicitly outlines, thus ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
The Air Waybill is a document used in air freight that functions similarly to a Bill of Lading. It serves as a contract between the shipper and the airline, providing details about the shipment. While both documents include information about the goods and shipping terms, the Hazard Bill of Lading includes additional stipulations regarding hazardous materials, ensuring that all safety protocols are followed during air transport.
In the realm of international shipping, the Dangerous Goods Declaration is another document that parallels the Hazard Bill of Lading. This declaration is required for the transport of hazardous materials and outlines the nature of the goods, including their classification and handling requirements. Like the Hazard Bill, it ensures compliance with safety regulations. However, the Dangerous Goods Declaration is more focused on the specifics of the materials being shipped, while the Hazard Bill of Lading encompasses broader shipping terms.
The Certificate of Origin is a document that certifies the country of origin of the goods being shipped. While it does not directly relate to hazardous materials, it is often required alongside shipping documents, including the Hazard Bill of Lading. Both documents ensure compliance with trade regulations, but the Certificate of Origin does not address the specific safety requirements associated with hazardous materials.
The Packing List is another document that complements the Hazard Bill of Lading. It provides a detailed account of the contents of each package being shipped, including weights and dimensions. While both documents are crucial for the shipping process, the Packing List does not include the safety measures and regulations that the Hazard Bill mandates for hazardous materials, making the latter more specialized.
The Export Declaration is a document required for shipments leaving the country. It provides information about the goods being exported, including their value and destination. While it shares some similarities with the Hazard Bill of Lading in terms of required details, the Export Declaration does not specifically address the handling of hazardous materials, which is a critical aspect of the Hazard Bill.
The Customs Invoice is another document that plays a role in international shipping. It provides information about the shipment for customs purposes, including the value and description of goods. While it is essential for clearing customs, it does not encompass the safety regulations and handling procedures that are outlined in the Hazard Bill of Lading for hazardous materials.
Lastly, the Delivery Receipt is a document signed upon receipt of goods, confirming their delivery. While it serves as proof of delivery, it does not contain the detailed information or safety requirements found in the Hazard Bill of Lading. The Hazard Bill is vital for ensuring that hazardous materials are transported safely and in compliance with all regulations, whereas the Delivery Receipt is a more straightforward acknowledgment of receipt.
Other PDF Forms
Aia Statement of Qualifications - The A305 format is simple and straightforward for easy completion.
Waiver of Lien to Date Chicago Title Pdf - The form must be signed in the presence of a notary to enhance its legal standing.
In addition to understanding the significance of the California Notary Acknowledgement form, it's essential for practitioners to access all relevant resources that facilitate this process. For comprehensive guidelines and examples, refer to All California Forms, which provide valuable information for ensuring that all legal documents adhere to the necessary standards of notarization.
Roof Inspection Template - Damage from natural disasters is excluded from the certification coverage.